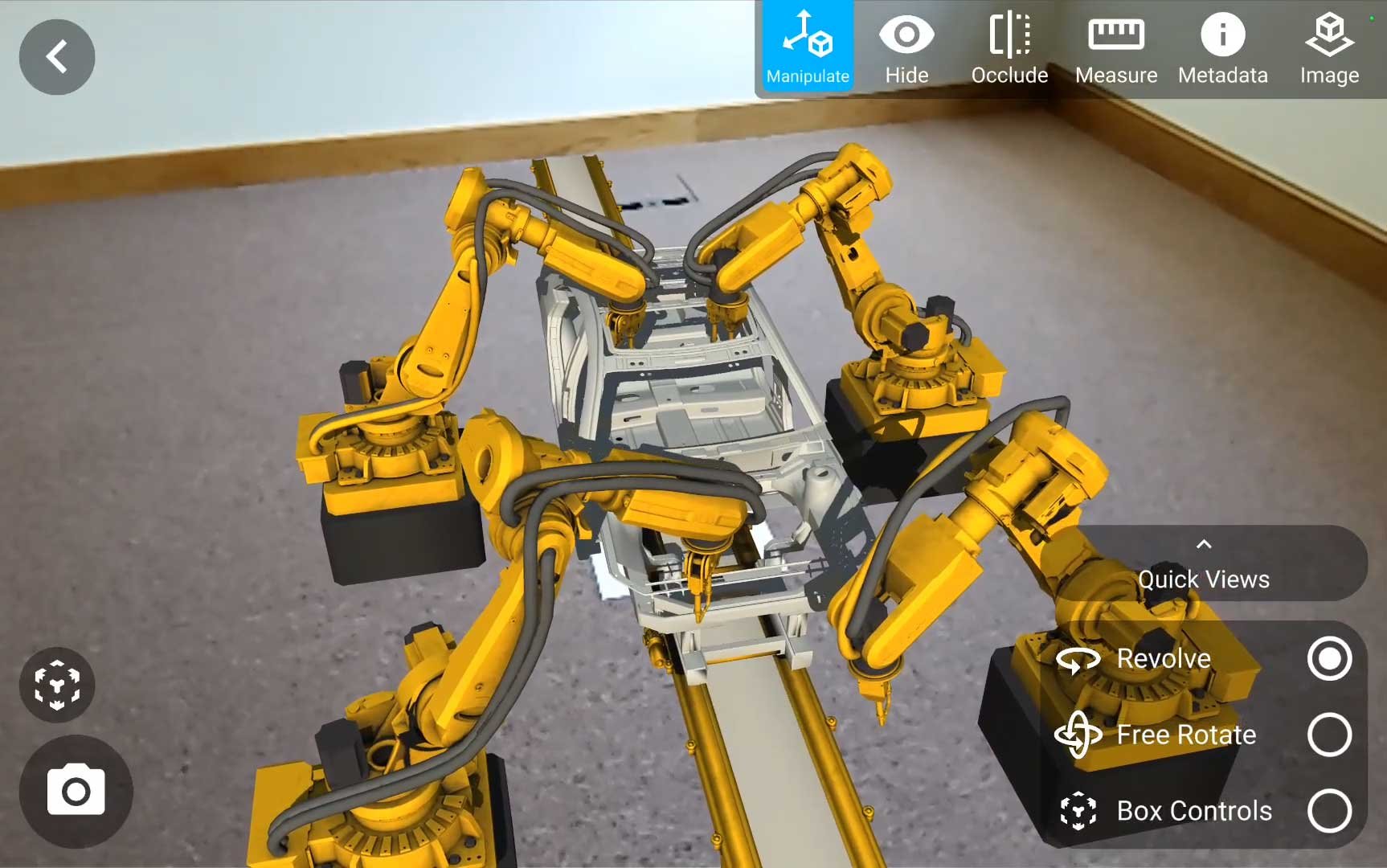
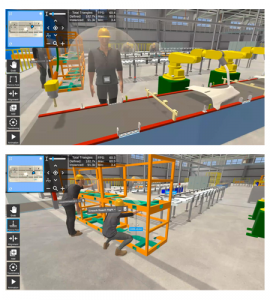
In the world of pharma manufacturing, precision is key. To execute flawlessly, pharmaceutical scientists and operators need the proper training and tools to accomplish the task. User-friendly augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (XR) technology that can provide workflow guidance to operators is invaluable, helping name brand companies get drugs, vaccines, and advanced therapies to patients faster.
AR has been a cost-effective way to improve training, knowledge transfers, and process execution in the lab during drug discovery and in the manufacturing suite during product commercialization. Apprentice’s AR Research Department is now seeing greater demand within the pharma industry for XR software capabilities that allow life science teams to use 3D holograms to accomplish tasks.
For example, operators are able to map out an entire biomanufacturing suite in 3D using XR technology. This allows them to consume instructional data while they work with both hands, or better understand equipment layouts. They can see and touch virtual objects within their environment, providing better context and a much more in-depth experience than AR provides.
Users can even suspend metadata in a 3D space, such as the entrance to a room, so that they can interact with their environment in a much more complete way, with equipment, objects and instruments tethered to space. Notifications regarding gowning requirements or biohazard warnings for example will automatically pop up as the operator walks in, enriching the environment with information that’s useful to them.
“It’s all about enhancing the user experience,” Linas Ozeratis, Mixed Reality Engineer at Apprentice.io. “At apprentice, our AR/XR Research Team has designed pharma-specific mixed-reality software for the HoloLens device that will offer our customers an easier, more immersive experience in the lab and suite.”
Apprentice’s XR/AR Research Team is currently experimenting with new menu design components for the HoloLens device that will reshape the future of XR user experiences, making it easier for them to interact with menus using just their fingers.
Apprentice’s “finger menu” feature allows users to trigger an action or step by ‘snapping’ together the thumb and individual fingers of the same hand. Each finger contains a different action button that can be triggered at any time during an operator’s workflow.
“Through our research, we’ve determined that the fingers are an ideal location for attaching AR buttons, because it allows users to trigger next steps without their arm or hand blocking the data they need,” Ozeratis added. It’s quite literally technology at your fingertips.”
Why does the pharma industry want technology like this? Aside from the demand, there are situations where tools like voice commands are simply not feasible. The AR Research Team also learned that interactive finger menus feel more natural to users and can be mastered quickly. Life science teams are able to enhance training capabilities, improve execution reliability and expand the types of supporting devices they can apply within their various environments.
“Introducing these exciting and highly anticipated XR capabilities is just one stop on our roadmap,” Ozeratis adds. “There are bigger and bolder things ahead that we look forward to sharing as the pharma industry continues to demand more modern, intelligent technologies that improve efficiency and speed.”